Employee Retention and Talent Analytics in Talent Management (Article 08)
Human resource is the bedrock of any organization; they are a vital and significant resource that helps give the organization an edge. Technologically generated data is needed for the analysis of human resources from the point of candidate attraction to the point of employee retention. Imperatively, for organizations to determine how far they want to imbibe talent analytics will indicate plans that will effectively develop their workforce with the right competencies, and this in turn becomes a booster to retaining employees. Development in the economy has resulted in stiff Labour competition creating avenues and opportunities for human resources. The biggest challenge organizations are faced with is managing these resources and retaining them, especially talented employees.
Attracting and retaining these skilled employees plays an important role for any organization as employees’ knowledge and skills are central to organizations’ ability to be economically positioned and competitive. Organizations are also saddled with continuously satisfying the employees so as to make them stay put. Sensitivity on the part of the organization with respect to employee retention is key, hence the study of a technology-driven talent management strategy to help understand the measures for employee retention.
The world is moving at a fast pace with technology. Technology as a tool has come to stay and enhances every discipline of which human resources is one: from human resource information systems to talent analytics. Talent analytics is a relatively new but exciting and growing area in human resources practices. Talent analytics is a creative initiative for transforming human resources-oriented organizations. It is the application of technology and expertise to the data of employees for better decisions making for the organization (Guenole et al, 2017). Talent analytics is capable of helping the manager retain top-performing employees, understand why they are loyal at the workplace, appreciate their satisfaction on the job, and peek into why they stay put. Talent analytics helps to determine corrective actions in addressing retention issues in the organization. A well-measured performance helps to identify prime candidates and increase satisfaction on the job which boosts employees’ loyalty to the organization. Talent analytics has become a powerful predictive tool that can help anticipate performance levels; it increasingly has become an indispensable tool for attracting, retaining, and optimizing workplace talent.
Schiemann et al (2018) believe that the key to human resources concern for businesses is employee retention (reducing employee attrition and turnover). There are significant financial and intangible costs associated with losing loyal and high-performing employees; it takes investments to find, hire, and train replacements. There is also a negative impact on the stakeholders they worked with regularly such as suppliers, colleagues, and customers. Hence, there is a call for organizations to retain talent in this technological era. Talent analytics or human resources analytical practice is as old as the late 19th century with credit to Fitz-enz (2010), author and president of the human resource services organization Saratoga Institute, he looked at the measures of human resources management, a seminal tome outlining the metrics that are put into use for effectively measuring of employee performance. Giving rise to talent analytics and how it has evolved from being just an experimental approach to improving employee satisfaction and loyalty: a total boost of employee retention.
Talent analytics gathers workforce data, from work history to performance management, to employee satisfaction and loyalty. The analyses aid manager’s insight in making critical decisions, curbing and totally eliminating high attrition rates. The world is moving at a fast pace with technology. Technology as a tool has come to stay and enhances every discipline of which human resources is one; from human resource information systems to talent analytics. According to Rory (2016), a human resources manager and blogger believe that “talent analytics is the real deal with its capable ability in successfully predictive and prescriptive analytics to recruit talent, identify and nurture talent’s strengths, and ensure sustained productivity and innovation through the use of initiations that recognizes and rewards performance.
Talent analytics has become a powerful predictive tool that can help anticipate performance levels; it increasingly has become an indispensable tool for attracting, retaining, and optimizing workplace talent. Although organizations are still struggling to understand the complexities of the potential of their employees, Managers are saddled with the responsibility of talent acquisition, retention, and encouraging performance and loyalty of the employees at the workplace in return employees must feel a sense of satisfaction (Becker et al, 2003).
According to Deloitte (2017), setting up clean and accurate data streams is, and will remain, a challenge for talent analytics. He further added that organizations run specific data quality activities to make the data fit for analysis with greater effectiveness directed at key variables that predicts and limits employee attrition: in order to ensure that predictive retention models are a robust tool for decision-making, steps must be taken for an accurate data stream. The reasons for which employees leave the organization are essential for building models that lead to targeted and effective retention strategies. Organizations must identify adequate coaching and mentoring for employees. Human resources managers are being trained on the key objectives of developing attrition models and coached on how to use generated information to avert high-flyers and performing employees from leaving the organization (Becker et al, 2006).
Concept of Talent Analytics
Talent analytics is the use of statistics, technology, and expertise to large sets of people data for adequate and timely decision-making for an organization. Talent analytics makes data accessible to enable reporting on demand (Wang &Cotton, 2018). Organizations apply talent analytics as the focus is on data for turnover and attrition (records of those who leave and if such separation was by choice) and the data gathered aids human resources managers know why employees left to accurately predict such attrition risks of existing employees; with the right knowledge and information steps can be taken to mitigate attrition and attain talent employee satisfaction. According to Bhatla (2011), organizations that will win in the future entail a change in strategy, an empowered human resources team in developing employees, and improving the organization’s performance.
Talent analytics can also be referred to as human resource analytics, workforce analytics, human capital analytics, or even just people analytics. Talent analytics improves an organization’s human resource procurement process, helping human resources managers to identify highly rated and qualified candidates (Comb et al, 2006). Talent analytics enhances the capabilities of the organization to generate and sustain a greater employee level of belongingness in the overall productivity and output of any organization; it shows organizations that are focused on retaining skilled and competent heads (talents). Successful talent analytics is one that is designed to grow a competent workforce for the attainment of a goal and build a competitive edge in the global face of business world (Sparrow et al, 2015). Levenson (2018) further explains that talent analytics is meaningfully developed following a careful diagnosis of the critical problems facing the organization.
The goal of any analytic solution is to provide organizations with information that can propel actionable perceptions for smarter decisions making for improved productivity and better results in the organization. It is imperative for managers to understand what solutions and decisions each analytics expression proffers and to match such analytical functions to the overall organization’s operational capabilities. Robinson (2018) provides a very useful contribution to the very high proportion of practitioners wishing to incorporate survey data into their analytics efforts. His comprehensive guide to the development and use of multi-item psychometrics scales for Talent Analytics is likely to become widely used in the Talent Analytics profession. The various dimensions of talent analytics build on each other descriptive analytics retrospectively view data that can be diagnosed to ascertain its usefulness for forecasting likely futurist predictions for which prescriptions are made for better results. These dimensions are interwoven with a focus on improving the capabilities of organizations in understanding data, and the development of such data for business decision making.
Descriptive Analytics – Viewing the Past
Asking “What has happened? When, where, and how?”, descriptive analytics sources data to provide trending information on past or current events that can give futuristic actions that are explained by the use of key performance indicators, descriptive analytics drills down into data to uncover details such as the frequency of events, the cost of operations and the root cause of failures. The most common type of analytics used by organizations is that it displays information within a report. Descriptive analytics provides a holistic view and context for what has happened in the past from the point of current status by gathering information regarding a problem from different sources, and comparing and contrasting data for diagnosis (Boudreau et al, 2017).
Descriptive analytics uses a full range of data to give a precise depiction of what has occurred in a business and how it varies from similar periods. These performance metrics can be used to indicate areas of strength and weakness; it also informs management of employees’ relevance and competence on the job (Fitz-Enz, 2010).
Diagnostic Analytics – Dissecting the past
Diagnostic analytics is a form of advanced analytics that examines past data to answer the question of “Why did it happen? Where should we look?”, and is categorized by techniques such as drill-down, data discovery, data mining, and correlations (Simon et al, 2018). Diagnostic analytics takes a deeper look at data to attempt to understand the causative proceedings and actions based on historical data. Descriptive analytics provides insights into outcomes from the past for diagnoses in order to ascertain the root cause of issues in the systems. Hence, organizations can take better decisions in avoiding the errors that resulted in negative outcomes from the past. Based on this historic analysis, organizations must identify areas that require further study.
According to Fitz-Enz (2018), a diagnostic analyst identifies the data sources to aid the explanation of these anomalies from descriptive analysis and then looks out for patterns outside the existing data sets in external sources to identify correlations to determine the cause of the problem. Hidden relationships are uncovered by looking at events that might have resulted in the identified anomalies. Probability theory, regression analysis, filtering, and time-series data analytics can all be useful for uncovering hidden issues in the data. Descriptive and diagnostic analytics uses insights from the past to provide detailed reports for futuristic plans.
Predictive Analytics- Understanding the Future
Asking “What could happen? What is the pattern”, predictive analytics provides answers that move beyond using historical data as the principal basis for decisions, it goes further in helping managers anticipate likely scenarios for proactively planning ahead instead of reacting to what has already happened. Predictive analytics utilizes diagnostic information accumulated over time for predicting outcomes (Fitz-Enz, 2010). Predictive capabilities such as forecasting and simulation provide enhanced insight that managers can use to make informed decisions.
Predictive analytics give organizations the capability to leverage their data for evaluation purposes for productivity anticipation or likelihood of failure (Davenport et al, 2010).
Prescriptive analytics – Tender Possible Solution
Asking “What should we do? What is the best action? What if we try this?” prescriptive analytics explores a set of possible actions and suggests actions based on descriptive, diagnostic, and predictive analyses of complex data. Prescriptive analytics provides reliable solutions for organizational needs and for better decision-making on alternative problems solving (Guenole et al, 2017). The outcomes help the organization identify inventory that should be re-ordered, talent deficiency in the organization due to attrition and turnover, measures to revamp a sale outlet, etc. Prescriptive analytics takes uncertainty into account and recommends ways to mitigate the risks that can result from it: Its ability is not only to examine potential outcomes but also to make recommendations to help managers make decisions even when the data environment is too large or complex.
Concept of Employee Retention
Employees today are different. They are not the ones who do not have good opportunities, especially, talented, skilled, competent, and experienced ones. Job dissatisfaction or lack of advancement opportunities, salary, remuneration, and others are the reasons why employees switch organizations (Schiemann et al, 2018). The resultant effect of employee attrition or turnover is loss of invested resources on the part of employers, employee/customer relationships are strained, and the huge cost associated with replacement and downturn of morale for remaining staff. It is therefore very imperative that employers retain their employees, especially the talented and experienced ones.
Over the years, the business statistics on employee participation, workplace wellness, work-life balance, and other topics has tailored towards indicating a strong interest in and recognition of how other aspects of working life influence people’s decisions to stay with or leave a company (Hom & Griffeth, 2000). There are numerous factors that create satisfaction that results in employee retention in an organization: factors such as:
A stimulating work environment - An environment that improves the effective use of people’s skills and knowledge, allowing them some degree of independence on the job; this will aid in providing an avenue for the employees to contribute more ideas, as they see how their contributions influence the overall well-being of the organization.
Opportunities for learning and upgrading skills - Development and consequent advancements in tasks require some level of learning for improvement. Effective communication and employee participation in decisions that affect them are attained when they are given room for improvement and contribution; understandings of what is happening in the organization are the employer’s main business concerns.
Good compensation and adequate, flexible benefit plan - Helping employees stay motivated with extrinsic values that propel them internally.
Recognition on the part of the employer - Every employee needs to strike a good balance between their lives at work and outside of work. Respect and support from peers and supervisors are significant in achieving such balance (Hamid et al, 2014).
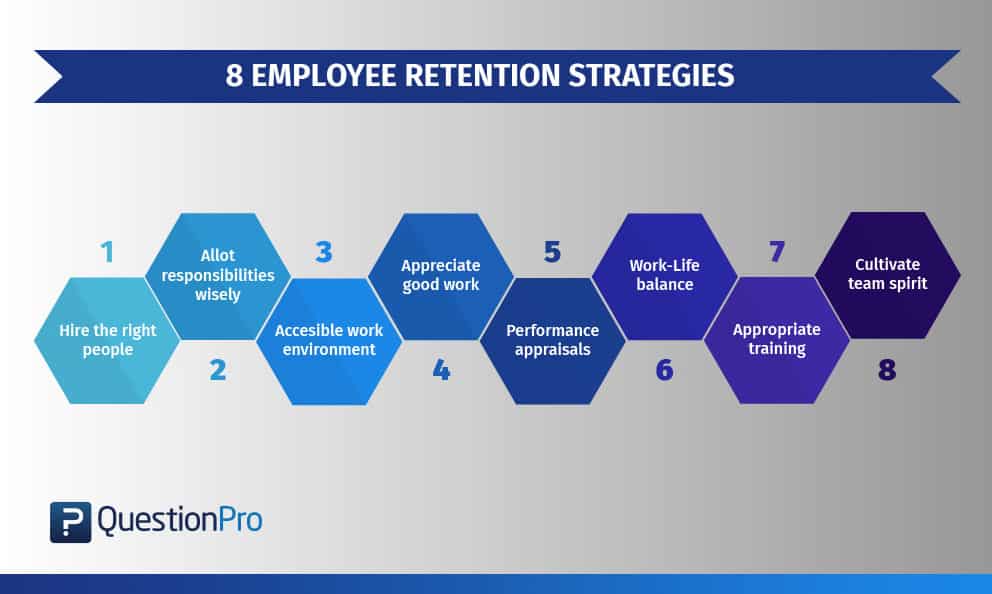
Employee Retention Strategies
Strategies here refer to a more formal and deliberate system of practices that links with an organization's overall vision, set of values, and mission (Allen, 2008). Organizations develop activities that engage in elaborate planning mechanisms for a cohesive strategy that deals with employee retention issues. According to Schiemann et al (2018), they emphasized the importance of good retention and the ability for organizations to keep their talents longer. To this employee retention strategies include employee engagement, employee training, employee motivation, and work-life balance.
Employee Engagement
The success or failure of the organization is largely dependent upon the employees working in it (Khan, 2013). Employee engagement is considered an important mechanism that is implored in the business world afloat. Kahn (2013) defined employee engagement as the dedication and involvement of the employees toward their organization and its value. Becker et al (2001) he saw employee engagement “as willingness or enthusiasm that the employee holds to spend optional effort towards the job”. Hamid et al (2014) define employee engagement as the extent to which an individual is attentive and absorbed in the performance of his/her roles. It is the positive feeling that employees have towards their jobs and also the motivation and effort they put into it.
An engaged employee is considered the base of organizational development. Such kind of employees carries the organization in a positive direction. They not only perform their work but also play an important role in achieving the organization’s goals and objectives. Engaged employees want to use their talent and strength to move the organization forward: performing tasks with passion and driving innovation on overall performance (Bakkar, 2008).
It is very important for the effective utilization of human resources and the smooth running of the organization. Without employee engagement, an organization cannot survive for a long period of time. As opined by Becker et al (2003) engaged employees strengthen the organizations’ competitive advantage and generate a favorable business environment. Cook (2008), has reported that engagement is one of the important and powerful strategies to attract, nurture, retain, respect, and manage the manpower of the organization. They have also pointed out that married employees tend to have a higher level of engagement than those who are unmarried.
Employee Training
In addition to employee engagement, training is another key area in retaining employees (Sundaray, 2011). Employees who enhance their skills through training are more likely to engage fully in work and have a tendency to be highly motivated and satisfied with mastering new tasks (Swarnalatha & Prasanna, 2012). According to Khan (2013), training and developmental activities are important and like every other human resource function, it improves the abilities of any employee. Training provides opportunities to raise talents in the organization; helping the employee to perform their work efficiently and effectively, hence reducing the problem of employee attrition and turnover.
Lack of skills has been cited as one of the reasons for employee turnover, thereby indicating the necessity for training, re-training, and multi-skill training. Messmer (2000) stressed that one of the important factors in employee retention is investment in employee training and career development. Organizations are most likely to productively retain their skilled employees when they invest in training and development. The return on such investment is growth and profitability. Tomlinson (2002) agrees with the view that organizations can keep the leading edge in this competitive world by having their employees well-trained in the latest technologies. Garg & Rastogi (2006) explained that in today’s competitive environment employee feedback is very essential for organizations; as they learn and gain knowledge, the more they will perform on the job to meet the global challenges of the marketplace. Handy (2008) has mentioned that proper innovation, and assimilation of new knowledge are essential for survival in any work environment. Thus, knowledge is the most expensive asset of any firm.
Employee Motivation
The challenge for any manager is to find the means to create and sustain employee motivation. On one hand, managers should focus on reducing job dissatisfaction (working conditions, salary, supervision, relationship with colleagues), while on the other hand should use motivating factors such as achievement, recognition, responsibility, and the work itself to retain competent employees. If employees feel appreciated for their achievements on the job and are involved in decision-making, their enthusiasm is fed and the resultant effect is motivation that will lead to productivity and continuous loyalty.
Organizations want to use the maximum potential of their human resources, to stay in the competition and to survive; great organizations are built on the inherent value of their human resources, and the motivation and commitment of their employees (Mohsen et al., 2004). To achieve employee satisfaction and commitment, effective motivation becomes a necessity (Tella et al., 2007). Mohsen et al. (2004) supposed that employee motivation and commitment are very important for an organization’s success. Motivated and committed employees with high levels of job involvement are considered an important asset to an organization. Barkar et al (2008) argued, that keeping employee motivation, commitment, and job involvement up, is always rewarding to a business; as motivated and committed employees are productive and emotionally stable. Motivation is a management process that encourages employees to work better for the overall benefit of the organization.
Work-Life Balance
Work-life balance is becoming gradually more central for employees and tends to affect employees’ decision to stay or leave an organization. Work-life balance is a concept that supports employees' flexible work schedules which allow them to take care of both their personal and professional life. The balance between personal and professional lives is determined by the amount of sacrifice the individual is ready to make at the expense of other areas of life. Loan-Clarke et al (2010) observed that a job that gives the holder the possibility to fulfill his/her family responsibilities/obligations increases such employees’ retention rate.
The relationship between retention and work-life balance is an area of concern as employees' focus is divided when time is not allotted to their personal life. Lener et al (2006) is of the view that employers should implement a harmonious balance to improve employee retention rate. Osman (2013) found that offering emotional support to employees through work-life balance reduces their intention to quit their job. Mita et al (2014) observed a direct relationship between employees’ decision to stay or leave is work-life balance.
Employee Retention through Talent Analytics
The need for organizations to retain their talents is crucial as their ability to remain in business depends largely on it (Garvin, 2013). Traditionally talent analytics are descriptive in nature, an examined employee data across dimensions such as department and demographics to identify past patterns within metrics like employee turnover and retention. The findings are used to formulate talent retention policies. Descriptive analytics do not predict future outcomes, the outcomes are diagnosed to know the reasons for past results, and predictive analytics goes a step further using the evidence from descriptive and diagnostic analytics as inputs for advanced techniques like statistical modeling, machine learning probability, regression analysis, and time series.
These methods provide forward-thinking measures to quantify the likelihood of an employee's leaving the organization within a certain period of time and prescriptive analytics proffers a mechanism that helps the organization keep skills within. Predictive analytics also identifies hidden connections between key factors contributing to employee turnover. The predictor variables such as pay, promotion, performance reviews, time spent at work, commute distance, relationship with a manager, training, ability to strike a balance with professional and personal life, motivation level, and engagement rate are contributory factors for employee retention or turnover. Organizations also use external data such as labor market indicators and the current economic scenario in prescriptive analytics to better design effective interventions for employee retention purposes (Bhatla, 2011).
It is important that organizations understand the dimensions of analytics as it is the tool that aids in problem identification and also brainstorms solutions using data-driven factors. Talent analytics helps organizations perceive challenges and also put a reward system that motivates talented employees to stay put in the organization. It identifies the key drivers of resignation and develops a retention measure. In this era, organizational success is hinged on the level of technology.
References
Guenole, N, Ferrar, J, & Feinzig, S. (2017).The power of
people: Learn how successful organizations use Talent Analytics to improve
performance. New York: Pearson.
Schiemann, W. A, Seibert, J. H, & Blankenship, M. H.
(2018). Putting human capital analytics to work: Predicting and driving
business success. Human Resource Management, 57(3), 795–807.
Fitz-Enz, J (2010).The New HR Analytics: Predicting the
Economic Value of a Company’s Human Investment. First Edition Amcom Books.
Rory, C. T (2016). Employee Engagement, HR Strategy, Talent
Management. https://rorytrotter.com/2016/08/31/examining-the-impact-of-ratingless-reviews-and-year-roundfeedback-on-employee-performance/
Becker, B. E, & Huselid, M. A. (2003). Measuring HR's
Performance? Benchmarking is Not the Answer! HR Magazine, 1(1), 57–61.
Deloitte. (2017).Rewriting the rules for the digital age:
2017 Deloitte human capital trends. New York: Deloitte University Press.
Becker, B. E, & Huselid, M. A. (2006). Strategic human
resources management: Where do we go from here? Journal of Management, 32(6),
898–925.
Wang, L, & Cotton, R. (2018). Beyond Moneyballto social
capital inside and out: The value of differentiated workforce experience ties
to per-formance. Human Resource Management 57(3), 761–780.
Bhatla, N. (2011). To study the employee engagement
practices and its effects on employee performance with special reference to
ICICI and HDFC bank in Lucknow. International Journal of Scientific &
Engineering Research, 2(8), 1- 7.
Combs, J, Liu, Y, Hall, A, & Ketchen, D (2006). How much
do high-performance work practices matter? A metaanalysis of their effects on
organizational performance. Personnel Psychology, 5(9), 501–528.
Sparrow, P. R, &Makram, H. (2015). What is the value of
talent management? Building value-driven processes within talent management
architecture. Human resource management review, 25(3), 249-263.
Boudreau, J., & Cascio, W. (2017). Human capital
analytics: Why are we not there? Journal of Organizational Effectiveness:
People and Performance, 4(2), 119–126.
Simón, C & Ferreiro, E. (2018). Workforce analytics:
case study of scholar-practitioner collaboration. Human Resource Management,
57(3), 781–793.
Davenport, T. H, Harris, J. G, & Morison, R.
(2010).Analytics at work: Smarter decisions, better results. Boston: Harvard
Business School Press.
Guenole, N, Ferrar, J, & Feinzig, S. (2017).The power of
people: Learn how successful organizations use Talent Analytics to improve
performance. New York: Pearson.
Hamid, S, & Farooqi, A. R. (2014). Taj group of hotels
as brand employer: A selective study of students as job aspirants at Aligarh,
India. International Journal of Tourism and Travel, 7(1 & 2), 23-30.
Becker, B. E, Huselid, M. A., & Ulrich, D. (2001).The HR
scorecard: Linking people, strategy and performance. Cambridge, MA: Harvard
Business Press.
Bakkar, A. B, & Scheufeli, W. B. (2008). Positive
organizational behaviour: Engaged employee in flourishing organizations.
Journal of Organizational Behaviour, 29, 147-154.
Cook, S. (2008). The essential guide to employee engagement
better business performance. Great Britain: Kogan Page Limited
Garvin, D. A. (2013). How Google sold its engineers on management. Harvard Business Review, 2(1), 75–82.
This text provides a comprehensive and insightful perspective on the pivotal role of talent analytics in the ever-evolving realm of human resources. It effectively highlights the impact of technology and data-driven insights in attracting, retaining, and optimizing workplace talent. The author skillfully navigates through the complexities of employee retention and the critical need for organizations to harness talent analytics for making informed decisions. The emphasis on accurate data streams, predictive analytics, and the interconnectedness of employee satisfaction and loyalty showcases a deep understanding of the subject matter. A well-articulated and enlightening piece indeed!
ReplyDeleteHi Prasadini,
DeleteThanks for your reply. Due to the huge differential value created by a talented employee, recent research in the human resource area tends to focus on the retention of talented employees rather than of entire workforce. No organization can even imagine the hazards of losing top talent, especially to its rival organization. At times, even a single employee can change the destiny of the organization. The benefits of talent analytics in terms of value creation are clear. For instance, if an organization can identify a causal relationship between training expenditure and profitability, then it is possible for the organization to set up a training strategy that may have a quantifiable impact on profitability. In spite of its potential benefits, the emergence of talent analytics as a separate field of business analytics has been very slow (CIPD 2013; OrgVue 2019). In the 2014 Global Human Capital Trends survey commissioned by Deloitte, surveyed businesses indicated that they understood the importance of building their talent analytics capabilities, but also revealed significant gaps in their current readiness.
This comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDeleteI really enjoyed reading this insightful blog post on talent analytics and employee retention in talent management. Every paragraph clearly demonstrates the author's thorough understanding of the subject. They do an amazing job of distilling complex ideas into insights that are simple to understand. The blog offers helpful advice on utilizing talent analytics to produce better results in addition to giving readers a thorough understanding of the significance of employee retention. Congratulations to the author for creating such a gem that is unquestionably required reading for anyone working in the HR or talent management fields! 👏👏
ReplyDeleteHi Malik,
DeleteThanks for your reply. Leveraging talent analytics is crucial for achieving superior results and gaining a comprehensive grasp of the significance of employee retention. By harnessing data-driven insights, organizations can identify high-performing individuals, foresee workforce trends, and optimize talent allocation. Talent analytics empowers decision-makers to make informed choices about recruitment, development, and succession planning, ultimately leading to higher productivity and cost savings. Furthermore, it underscores the critical importance of employee retention in preserving institutional knowledge, reducing turnover costs, and maintaining a motivated, experienced workforce. Employee retention not only strengthens organizational stability but also enhances overall performance, making it a strategic imperative in today's competitive business landscape.
The article highlights the importance of human resources in organizations and the role of talent analytics in employee retention. It explains the four dimensions of talent analytics: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive. It also discusses strategies for employee retention, such as engagement, training, motivation, and work-life balance.
ReplyDeleteThe text highlights how data-driven insights can help organizations identify retention challenges and develop effective measures.
A Good Read
Hi Asanka,
DeleteThanks for your reply. Data-driven insights play a pivotal role in pinpointing retention challenges and formulating effective strategies. By analyzing employee data, organizations can detect patterns related to turnover, such as departments with higher attrition rates or common reasons for leaving. These insights allow for targeted interventions, like improved management training or adjustments to compensation structures. Additionally, predictive analytics can forecast potential retention issues, enabling proactive measures such as personalized career development plans or mentorship programs. By harnessing data, organizations gain a proactive and informed approach to employee retention, fostering a workplace where employees feel valued, engaged, and less likely to seek opportunities elsewhere.
The article effectively highlights the challenges organizations face in retaining talented employees in the competitive job market. It also emphasizes the role of factors like employee engagement, training, motivation, and work-life balance in creating a positive work environment that encourages employee retention.
ReplyDeleteAccording to Turner(2022), Retaining top talent and leveraging data-driven insights to make informed decisions can significantly contribute to an organization's success.
Agreed with most of the points in your article. Employee training and their motivation are important in the subject of employee retention. This is a good article for someone who is interested in reading Talent Analytics.
ReplyDeleteAlso, application of these analytics is really important for the leadership roles in a company.
Hi Aruni,
DeleteThanks for your reply. The application of talent analytics is exceptionally vital for leadership roles in a company. Leadership positions have a profound impact on an organization's success, making it crucial to identify and nurture the right talent. Talent analytics aids in assessing the potential of individuals, identifying leadership competencies, and predicting future performance. It enables data-driven decisions regarding leadership development, succession planning, and even recruitment strategies for leadership roles. This not only ensures that leadership positions are filled by the most capable individuals but also helps in grooming future leaders, ultimately strengthening the organization's capacity for innovation, adaptation, and long-term success.
This article does a wonderful job highlighting the importance of human resources in organizations and how technology, especially talent analytics, is playing a crucial role in managing and retaining employees. It explains how attracting and retaining skilled employees is essential for an organization's success and how technology-driven solutions like talent analytics are helping achieve this. The article also emphasizes the significance of clean and accurate data for effective talent analytics. Overall, it's a clear and insightful read that sheds light on how technology and human resources are coming together to shape the modern workplace positively. Great job!
ReplyDeleteHi Prasadini,
DeleteThanks for your reply. Technology and human resources are synergizing to enhance the modern workplace. HR tech solutions streamline recruitment, onboarding, and performance management, reducing administrative burdens. Data-driven insights help optimize employee engagement, development, and retention. Remote work technologies provide flexibility, promoting work-life balance. AI-driven tools improve decision-making and predict HR trends. This collaboration fosters a more efficient, inclusive, and employee-centric workplace, benefiting both organizations and their workforce in today's rapidly evolving business landscape.
Agreed, Employee retention means keeping employees happy and motivated to stay with a company, often achieved through strategies like training, work-life balance, and engagement. Talent analytics involves using data to understand why employees leave and how to make them stay, while employee training improves skills (Ford, D. G., 2017). Employee motivation encourages hard work, making them more likely to stay. These concepts aim to foster long-term employee commitment and productivity.
ReplyDeleteHi Gayani,
DeleteThanks for your reply. Yes, As per Ford, 2017, Talent analytics delves into data to comprehend the underlying reasons for employee turnover and to devise strategies to enhance retention rates. It identifies patterns and factors contributing to attrition, enabling organizations to proactively address issues such as dissatisfaction, lack of growth opportunities, or inadequate work-life balance. In contrast, employee training focuses on improving specific skills and knowledge. It equips employees with the competencies required for their roles, enhancing their proficiency, productivity, and overall contributions. Together, talent analytics and employee training form a comprehensive approach to nurturing a skilled, engaged, and loyal workforce while minimizing turnover and promoting organizational success.
Nice article. I concur with the majority of the assertions in your article. Employee training and fostering their motivation stand as pivotal aspects within the realm of employee retention. This article serves as a valuable resource for those intrigued by the domain of Talent Analytics. Furthermore, the utilization of these analytics is of paramount importance, especially in the context of leadership positions within a company.
ReplyDeleteHi Hisshanthi,
DeleteThanks for your reply. Yes, I agree with your point. The utilization of talent analytics is of paramount importance, particularly in the context of leadership positions within a company. Leadership significantly impacts an organization's success, making it crucial to employ data-driven insights in identifying and developing leaders. Talent analytics assesses leadership potential, predicts performance, and informs decisions regarding succession planning and leadership development programs. By aligning the right talent with leadership roles, organizations enhance their strategic capabilities, adaptability, and long-term sustainability. Talent analytics is, therefore, an invaluable tool for shaping a leadership team that can guide the company to thrive in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
Excellent article on employee retention and talent analytics! Your comprehensive breakdown of predictive and prescriptive analytics provides valuable insights for HR professionals. I particularly appreciate your focus on the importance of employee engagement, training, and motivation as key retention strategies. The way you've tied these elements back to analytics is enlightening.
ReplyDeleteCould you elaborate on how organizations can effectively use machine learning and statistical modeling in predictive analytics to foresee employee turnover?
Hi Ashinka,
DeleteThanks for your reply. Organizations can effectively employ machine learning and statistical modeling in predictive analytics to anticipate employee turnover by following these steps:
Data Collection: Gather comprehensive data, including employee demographics, performance history, job satisfaction surveys, compensation details, and exit interviews. This data forms the foundation for predictive analysis.
Feature Selection: Identify relevant variables that may influence turnover, such as tenure, promotions, job role, salary, work-life balance, and employee engagement scores.
Data Preprocessing: Clean and prepare the data, addressing missing values and outliers. Normalize or scale features as needed.
Model Selection: Choose appropriate machine learning algorithms, such as logistic regression, decision trees, random forests, or neural networks, based on the dataset and problem complexity.
Model Training: Utilize historical data to train the model, where it learns patterns and relationships between variables associated with employee turnover.
Validation and Testing: Split the dataset into training and testing subsets to evaluate model accuracy and generalization performance.
Deployment: Implement the predictive model in real-time HR processes to continuously monitor and identify employees at risk of leaving.
Feedback Loop: Regularly update the model with new data to maintain its accuracy and relevance.
Predictive analytics using machine learning and statistical modeling allows organizations to proactively address turnover risks by identifying key factors and taking preventive actions, thereby fostering a more stable and engaged workforce.
Hi Hasini, Great job explaining talent analytics and employee retention strategies! Can you share a real-world example of how talent analytics helped improve employee retention in an organization?
ReplyDeleteHi Nilantha,
DeleteThanks for your reply. IBM is an excellent example of an organization that leveraged talent analytics to enhance employee retention. Facing a high turnover rate in its call center, IBM applied data-driven insights to identify the factors contributing to attrition.
IBM's HR team collected and analyzed a vast dataset that included employee demographics, job roles, work hours, and performance metrics. Using predictive analytics, they discovered that employees with longer commutes and those working evening shifts were more likely to leave.
Armed with this knowledge, IBM implemented several targeted interventions. They adjusted work schedules to minimize late shifts, introduced flexible work arrangements, and offered transportation assistance for employees with lengthy commutes.
The result was a significant reduction in turnover, leading to substantial cost savings associated with recruitment and training. Moreover, employee morale and productivity improved, as the changes demonstrated IBM's commitment to addressing their concerns. This real-world example underscores how talent analytics can pinpoint retention challenges and drive effective, data-backed solutions.